Monitoring Sediment in Runoff Water system automatically measures runoff flow rate and sediment concentration, and calculates total runoff volume. It is suitable for soil and water conservation research and management. Based on electromagnetic and photoelectric principles, the system achieves continuous, unattended monitoring in all weather conditions.
Monitoring Sediment in Runoff Water is a specialized system deployed at the outlet of small watersheds or typical cross-sections for automated, continuous monitoring of key parameters of soil erosion. The core function of this system is to automatically measure surface runoff processes and simultaneously obtain data on sediment content in the runoff, thus providing direct evidence for quantifying soil erosion intensity and evaluating the effectiveness of soil and water conservation measures.
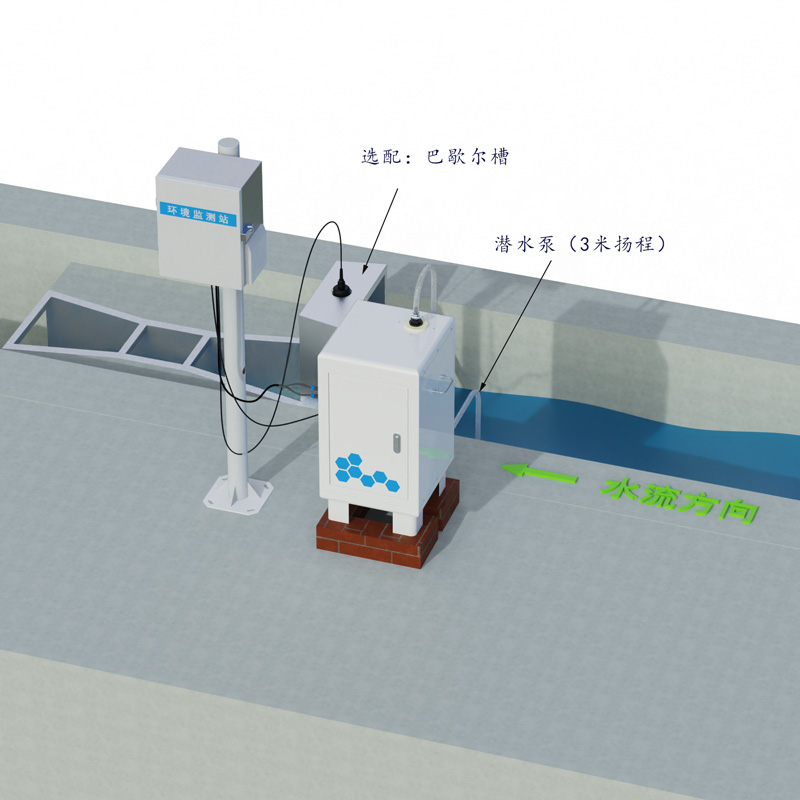
The system can automatically measure the runoff flow rate passing through the monitoring section. By measuring parameters such as water level and flow velocity, combined with preset cross-sectional shape data, the instantaneous flow rate can be calculated and output in real time. The data logger automatically integrates the continuous instantaneous flow rate data to calculate the total runoff volume within any specified time period after the start of rainfall-induced runoff. This flow data is fundamental for analyzing runoff patterns and calculating the total sediment transport.
Another core function of the system is the real-time collection of runoff sediment concentration data. Its sediment measurement technology is mainly based on two physical principles. One uses the principle of electromagnetic induction, indirectly determining sediment concentration by measuring changes in water conductivity. This method is more suitable for water bodies with stable electrolyte content. The other uses photoelectric sediment measurement technology, based on the principle of turbidity extinction law, where the attenuation of light intensity as it passes through turbid water has a definite relationship with the concentration of suspended sediment in the water. By emitting light of a specific wavelength and measuring the light intensity at the receiving end, the real-time sediment concentration can be calculated. Some systems combine both technologies to improve measurement accuracy and reliability.
The complete system typically consists of hydrological parameter sensors (such as water level gauges and flow meters), sediment concentration sensors, data acquisition and transmission modules, power supply units, and protective structures. The data logger automatically collects and stores flow rate and sediment concentration data at set time intervals (e.g., every minute). Through the built-in wireless communication module (such as 4G, Beidou), the data can be remotely transmitted to the monitoring center platform. The power supply system typically employs a combination of solar energy and high-capacity batteries to ensure continuous operation even during cloudy or rainy weather, meeting the requirements for 24/7 unattended monitoring.
This system primarily serves research, management, and practical applications in the field of soil and water conservation. In research, it provides long-term, high-resolution data series for soil erosion model calibration and validation, and comparative studies of the effectiveness of different soil and water conservation measures in reducing runoff and sediment. At the management level, water resources and soil conservation departments can utilize its networked monitoring data to dynamically understand regional soil erosion conditions, evaluate the effectiveness of key treatment areas, and provide quantitative evidence for soil and water conservation supervision and enforcement. In practical applications, the system can be deployed at the outlets of soil erosion control responsibility zones in mines, development zones, and large-scale construction projects to quantitatively monitor soil erosion during construction and operation.
This system represents a technological leap from the traditional discrete mode of manual, timed sampling and laboratory analysis to automated, continuous online monitoring. The continuous process data it acquires can more accurately reflect the dynamic process of soil erosion during individual rainfall events, particularly capturing the initial runoff peak, which usually has the highest sediment concentration. This is crucial for accurately calculating soil loss during a single heavy rainfall event. Monitoring Sediment in Runoff Water has become an important infrastructure in modern soil and water conservation monitoring systems.
Article address:https://www.sqqx.net/en/news/834.html

 +86 15898932201
+86 15898932201



